Autonomous Systems — How AI Will Drive the Future of Transportation

The transportation industry is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and autonomous systems. As cities grow and the demand for efficient, safe, and sustainable transportation solutions increases, autonomous vehicles (AVs) and intelligent transport systems are poised to reshape how we move. This blog explores the current landscape of autonomous systems, their potential applications, and their implications for society and the economy.
Understanding Autonomous Systems
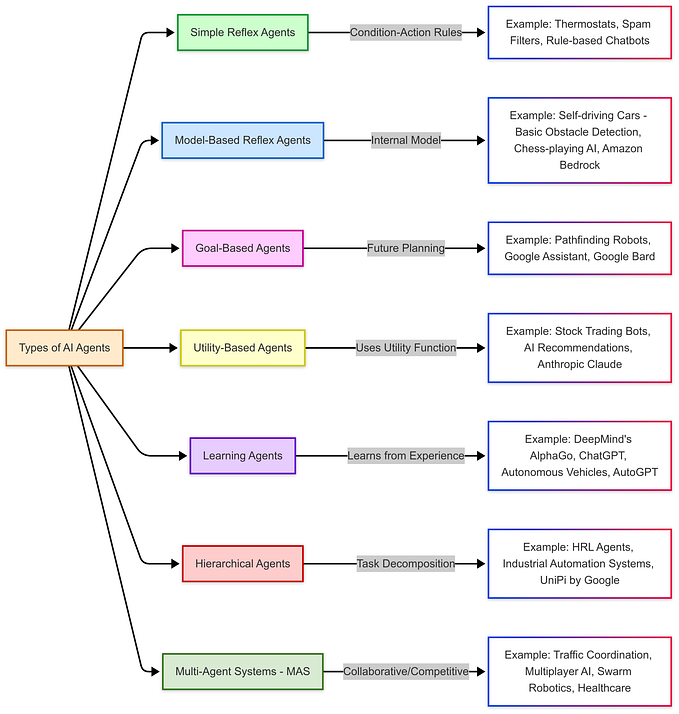
Autonomous systems refer to technologies that can perform tasks without human intervention. In the context of transportation, this includes vehicles equipped with AI algorithms, sensors, and advanced computing capabilities to navigate, make decisions, and respond to their environment.
Key Components of Autonomous Systems
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- Machine Learning: Algorithms that improve performance as they are exposed to more data, enabling vehicles to learn from experiences.
- Computer Vision: Technologies that allow vehicles to interpret visual information from the world around them, crucial for recognizing road signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
Sensors and Hardware:
- Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging): Uses laser light to create detailed 3D maps of the environment, helping vehicles understand their surroundings.
- Radar: Detects objects at longer distances and under various weather conditions, providing an additional layer of safety.
- Cameras: Essential for visual recognition tasks, cameras can capture images and videos for analysis by AI algorithms.
Connectivity:
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X): Communication systems that allow vehicles to interact with each other, infrastructure, and cloud services, improving traffic management and safety.
Current Applications of Autonomous Systems in Transportation
The integration of autonomous systems into transportation is already happening across various sectors. Here are some notable applications:
1. Autonomous Passenger Vehicles
- Ride-Hailing Services: Companies like Waymo and Cruise are testing and deploying autonomous ride-hailing services. These platforms allow users to summon driverless cars for transportation, reducing the need for personal vehicle ownership and enhancing urban mobility.
- Private Ownership: Major automakers, such as Tesla and Ford, are developing autonomous features for personal vehicles, allowing for semi-autonomous driving capabilities, such as highway autopilot and lane-keeping assistance.
2. Public Transportation
- Autonomous Buses: Cities are beginning to implement autonomous buses that can navigate fixed routes with minimal human oversight. For example, the Navya autonomous shuttles in Las Vegas and other cities offer safe and efficient transport in designated areas.
- Trams and Light Rail: Autonomous systems are also being tested in tram networks. For instance, in Dubai, the Roads and Transport Authority is exploring fully automated light rail systems to improve public transportation efficiency.
3. Freight and Logistics
- Self-Driving Trucks: Companies like Waymo and Aurora are developing autonomous trucking solutions to streamline freight transport. These trucks can operate on highways, reducing driver fatigue and increasing efficiency. Research by the American Transportation Research Institute suggests that automation could save the trucking industry billions annually through enhanced efficiency and reduced labor costs.
- Last-Mile Delivery: Startups such as Nuro and Starship Technologies are leveraging autonomous vehicles for last-mile deliveries. These small delivery robots can navigate urban environments to transport goods directly to consumers, minimizing the need for human delivery drivers.
Future Prospects of Autonomous Systems in Transportation
As technology continues to advance, several trends are shaping the future of autonomous transportation systems.
1. Regulatory Developments
- Frameworks for Safety: Governments are developing regulations to ensure the safe deployment of autonomous vehicles. For instance, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States is working on guidelines to facilitate the testing and deployment of AVs while prioritizing public safety.
- Insurance Models: As autonomous vehicles become more prevalent, insurance models will need to evolve. Companies may need to develop policies that address liability in cases of accidents involving AVs, shifting responsibility from drivers to manufacturers or software developers.
2. Integration with Smart Cities
- Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS): Autonomous vehicles will increasingly integrate with smart city infrastructure, optimizing traffic flow and reducing congestion. For example, traffic signals could communicate with AVs to improve their routes and minimize wait times.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Autonomous systems can collect vast amounts of data that cities can analyze to improve transportation planning and infrastructure investment, enhancing overall urban mobility.
3. Environmental Impact
- Sustainability Initiatives: Autonomous vehicles have the potential to contribute to sustainability goals by optimizing driving patterns and reducing emissions. Research by the International Energy Agency (IEA) suggests that widespread adoption of autonomous electric vehicles could significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions in urban areas.
- Shared Mobility Solutions: Autonomous ride-sharing services could reduce the number of vehicles on the road, leading to lower congestion and decreased pollution levels.
Challenges Facing Autonomous Systems in Transportation
Despite the promising prospects of autonomous systems, several challenges need to be addressed to realize their full potential.
1. Technical Limitations
- Safety and Reliability: Ensuring that autonomous systems can operate safely in diverse and unpredictable environments remains a significant hurdle. Accidents involving AVs, such as the 2018 incident with an Uber self-driving car in Tempe, Arizona, highlight the need for robust safety protocols and testing.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As vehicles become more connected, they also become vulnerable to cyberattacks. Ensuring the security of vehicle software and data transmission is crucial to prevent malicious interference.
2. Public Acceptance
- Trust and Perception: Building public trust in autonomous vehicles is essential for widespread adoption. Studies, such as those conducted by the Pew Research Center, indicate that while many people are optimistic about AVs, concerns about safety, job displacement, and ethical dilemmas remain prevalent.
- Education and Outreach: Public education initiatives will be vital in addressing misconceptions and promoting the benefits of autonomous systems. Engaging communities through demonstrations and information campaigns can foster acceptance.
3. Economic and Workforce Impacts
- Job Displacement: The rise of autonomous systems raises concerns about job losses in driving professions. Research from the Brookings Institution estimates that up to 25% of U.S. jobs could be threatened by automation, necessitating workforce retraining and upskilling programs.
- Economic Inequality: The benefits of autonomous transportation may not be evenly distributed. Ensuring equitable access to autonomous services, particularly in underserved communities, is essential for maximizing societal benefits.
Conclusion
Autonomous systems, driven by advancements in AI, are set to revolutionize the transportation landscape. With applications in passenger vehicles, public transit, and freight logistics, these technologies promise to enhance efficiency, safety, and sustainability in transportation. However, realizing the full potential of autonomous systems will require addressing technical, regulatory, and social challenges.
As we navigate this transformative era, collaboration among industry stakeholders, governments, and communities will be crucial in shaping a future where autonomous transportation systems serve the needs of all. By prioritizing safety, equity, and environmental sustainability, we can harness the power of AI to create a more efficient and accessible transportation ecosystem for future generations.